
When it comes to making a battery-powered application, choosing the right battery for your application becomes very crucial as it affects the overall performance and longevity of the whole system. When selecting a battery, there are several characteristics to consider such as battery capacity, voltage, battery chemistry, discharge rate, and operating temperature range of the battery. So, in this article, we have decided to discuss all these battery characteristics in detail to help you choose the right battery for your application.
Let’s Talk about Battery Properties, Common Form Factors, and Applications
Before we look at all the details of a battery, let’s clear out some simple and well-known facts about a battery; batteries can be categorized into two types, Primary Battery(batteries that cannot be recharged once depleted), and Secondary batteries (batteries whose chemical reactions can be reversed by applying a certain voltage to the battery).
The AA and AAA Batteries:
AA and AAA batteries are two of the most commonly used types of batteries in everyday electronic devices, and they come in both Rechargeable and Non-Rechargeable types. They are both small, cylindrical and have positive and negative terminals at opposite ends of the battery, as you can see from the image below.

If we are talking about the dimensions of AA and AAA batteries, AA batteries are larger than AAA batteries, measuring approximately 50.5mm in length and 14.5mm in diameter, while AAA batteries are smaller, measuring approximately 44.5mm in length and 10.5mm in diameter. Due to their size difference, AA batteries generally have a higher capacity and longer lifespan than AAA batteries. AA and AAA batteries are both available in different type of chemistries including alkaline, lithium, and rechargeable NiMH (Nickel Metal Hydride). Alkaline batteries are the most common type of AA and AAA batteries and are widely used in everyday devices such as remote controls, flashlights, and toys. Another most important factor is capacity of the battery, Alkaline AA batteries typically have a capacity ranging from 1,900mAh to 3,000mAh, while alkaline AAA batteries usually have a capacity ranging from 600mAh to 1,200mAh. Lithium AA batteries have a higher capacity than alkaline batteries, typically ranging from 2,400mAh to 3,300mAh. Lithium AAA batteries have a capacity ranging from 800mAh to 1,200mAh. Rechargeable NiMH AA and AAA batteries have a lower capacity than alkaline and lithium batteries, typically ranging from 600mAh to 2,500mAh. However, they can be recharged multiple times, making them a more cost-effective and environmentally-friendly option in the long run.
Applications of AA and AAA Batteries:
AA and AAA batteries can be used in many applications such as Remote Controls
Flashlights, Digital cameras, Portable radios, Toys, Wireless computer peripherals (such as wireless keyboards and mice), Clocks and alarms, Portable gaming devices, Portable speakers and many more.
[So here I can add a characteristic graph from the datasheet I need an opinion on this section]
For AA Alkaline batteries it will be:
Some description
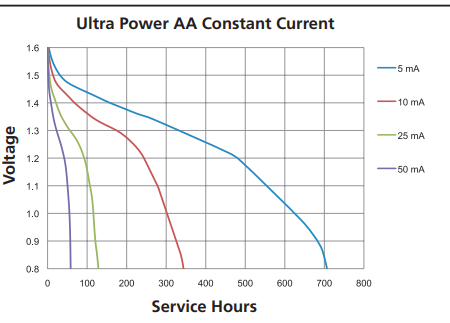
Finally, we will go like this, for more information please refer to the Datasheet of Duracell AA Battery
[And it will be for all AA and AAA chemistry that are available]
I can do this or I can say, Please Refer to the datasheet for more information and end it there.??
The Coin Cell Batteries:
Coin cell batteries are small, disc-shaped batteries that are commonly used in small electronic devices, such as watches, calculators, and hearing aids. They are also used in some medical devices, remote controls, and small electronic toys. And like other battery types, the coin cell also comes in rechargeable and non-rechargeable versions.

The Wikipedia doc on coin cell Batteries gives us a good idea about the variety of shapes and sizes the batteries are available. But among those are CR2032, CR2025, LR44, LR44, CR2450, CR1632, CR1616, SR626SW. If we are talking about its dimension, coin cell batteries are labeled with a code that represents their size. This code can be of two digits(for the standard case) or four digits (represents diameter and height). The first digit(s) of the code represents the outer diameter of the battery in millimeters, with exact diameters specified by the standard. For example, if the first digit is 9, the battery will have a diameter of 9.5mm. The last two digits of the code represent the overall height of the battery in tenths of a millimeter. This system ensures that there is no ambiguity in the size of the battery, making it easy to determine which battery is required for a particular device. An example could be,
- CR2032: lithium, 20 mm diameter, 3.2 mm height, 220 mAh
- CR2032H: lithium, 20 mm diameter, 3.2 mm height 240 mAh
- CR2025: lithium, 20 mm diameter, 2.5 mm height, 170 mAh
- SR516: silver, 5.8 mm diameter, 1.6 mm height
- LR1154/SR1154: alkaline/silver, 11.6 mm diameter, 5.4 mm height. The two-digit codes LR44/SR44 are often used for this size
The table below will give you a good idea about the code and diameter of the batteries in mm.
| Number Code | Nominal diameter in (mm) | Tolerance in(mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 4.8 | ±0.15 |
| 5 | 5.8 | ±0.15 |
| 6 | 6.8 | ±0.15 |
| 7 | 7.9 | ±0.15 |
| 9 | 9.5 | ±0.15 |
| 10 | 10.0 | ±0.20 |
| 11 | 11.6 | ±0.20 |
| 12 | 12.5 | ±0.25 |
| 16 | 16.0 | ±0.25 |
| 20 | 20.0 | ±0.25 |
| 23 | 23.0 | ±0.50 |
| 24 | 24.5 | ±0.50 |
| 44 | 11.6 | ±0.20 |
Now if we are talking about coin cell battery chemistry and their Application then there are a lot of options available to choose from but in this section let me give you the most commonly used coin cells and the list of applications they are used for
Lithium Manganese Dioxide (Li-MnO2): This is the most common type of coin cell battery. It has a nominal voltage of 3 volts and is commonly used in small electronic devices like watches, calculators, and remote controls. The CR2032 battery is one such example of a battery made with Lithium Manganese Dioxide battery.
Silver Oxide (AgO): Silver oxide batteries also have a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts and are commonly used in small electronic devices like watches, calculators, and medical devices. They have a longer shelf life and higher energy density than alkaline batteries, but they are also more expensive. The SR626SW battery, also known as the 377 battery or watch battery is one such example of a battery made with Silver Oxide.
Zinc Air (Zn-Air): These batteries use oxygen from the air as a reactant, which makes them ideal for hearing aids and other medical devices. They have a high energy density, but they are not rechargeable. The ZA312, ZA10 also known as the 312 battery are some examples of these batteries.
Lithium Ion (Li-ion): Li-ion coin cell batteries have a high energy density and a long cycle life. They are commonly used in small electronic devices like Bluetooth earbuds, smartwatches, and smartphones. The LIR2032 rechargeable battery is an example of a Li-ion battery.
Nickel-Cadmium (Ni-Cd): Ni-Cd coin cell batteries are rechargeable and commonly used in remote controls, small appliances, and power tools. The N200AA battery is a good example of a Ni-Cd battery.
Nickel-Metal Hydride (Ni-MH): Ni-MH coin cell batteries are rechargeable and commonly used in remote controls, small appliances, and digital cameras.An example of a Nickel-Metal Hydride (Ni-MH) coin cell battery is the NH35 or LR44 size Ni-MH rechargeable battery.
Alkaline-Manganese (AlMn): AlMn coin cell batteries are commonly used in small electronic devices like calculators and remote controls. An example of an Alkaline-Manganese coin cell battery is the LR44 or AG13 battery.
Zinc-Carbon (Zn-C): Zn-C coin cell batteries are commonly used in small electronic devices like calculators and remote controls. An example of a Zinc-Carbon coin cell battery is the LR44 or AG13 battery
Lithium Polymer (Li-Po): Li-Po coin cell batteries have a high energy density and can be molded into different shapes, making them ideal for small electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, and smartwatches. A common example of a lithium polymer coin cell battery is the CR2032 battery.
Lithium Sulphur Dioxide (Li-SO2): Li-SO2 coin cell batteries are commonly used in military and aerospace applications due to their high energy density and long shelf life. A common example of a lithium-sulfur dioxide coin cell battery is the LS14500 battery.
Lithium Thionyl Chloride (Li-SOCl2): Li-SOCl2 coin cell batteries are commonly used in military and aerospace applications due to their high energy density and long shelf life. A common example of a lithium thionyl chloride coin cell battery is the LTC-9C battery.
Different types of 9V Batteries:
9-volt batteries, also known as PP3 batteries, are rectangular batteries that are commonly used in a variety of devices, including smoke alarms, guitar pedals, and some handheld radios, Digital Multimeter. They are a type of primary battery, which means they are not rechargeable and must be replaced when they run out of power.

The standard dimensions of a 9-volt battery are approximately 48.5mm in height, 26.5mm in width, and 17.5mm in depth. They are typically made with an alkaline chemistry, which provides a high energy density and longer shelf life than some other types of batteries.

In recent years, some manufacturers have developed rechargeable 9-volt batteries, which can be a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective option for devices that use 9-volt batteries. However, rechargeable 9-volt batteries typically have a lower capacity and shorter shelf life than non-rechargeable 9-volt batteries, so they may not be suitable for all applications.
18650 and 14500 Batteries:
18650 and 14500 batteries are types of rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in a variety of electronic devices.

The 18650 battery is a cylindrical cell that measures 18mm in diameter and 65mm in length. It typically has a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts and a capacity of around 2000 to 3000 milliampere-hours (mAh). These batteries are commonly used in laptops, flashlights, and electric vehicles, whereas A 14500 battery is a type of rechargeable lithium-ion battery with a nominal voltage of 3.7 volts and a typical capacity of around 800 to 900 milliampere-hours (mAh). 14500 batteries are commonly used in flashlights, lasers, and other electronic devices that require a compact and high-capacity power source. They can also be used as a replacement for alkaline AA batteries in certain devices, although it’s important to note that their voltage is higher than a typical AA battery.
C and D Batteries:
C and D batteries are two common sizes of disposable alkaline batteries that are used to power a variety of electronic devices.
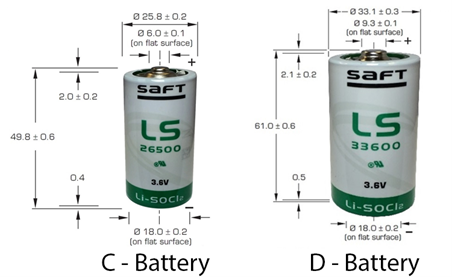
C batteries are cylindrical in shape and have a length of approximately 50 mm and a diameter of approximately 26mm. They typically have a voltage of 1.5 volts and a capacity of around 8000 milliampere-hours (mAh). D batteries, on the other hand, are larger and have a length of approximately 61mm and a diameter of approximately 34mm. They also have a voltage of 1.5 volts but have a larger capacity of around 20,000 mAh. Both C and D batteries are commonly used in devices that require higher levels of power and longer battery life than can be provided by smaller batteries such as AA or AAA batteries. Some examples of devices that use C and D batteries include flashlights, portable radios, and toys.


2 thoughts on “The Ultimate Battery Selection Guide: A Complete Guide to Choosing the Right Battery for Your Project”
It’s awesome forr me too have a web site, which is valuabble
in favr of mmy experience. thanks admin
Thank you for your kind words! Feel free to share the post and keep an eye out for more upcoming exciting content.